CELEBRITY
Six-Year-Old John-Henry diagnosed before he was born, Triumphs Over rare congenital heart condition Called Hypoplastic Left Heart Syndrome (HLHS) with Lifesaving Heart Transplant After Six-Month Wait”
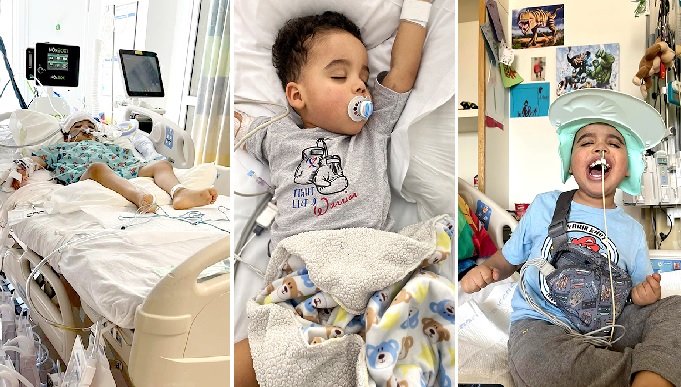
I’m getting a new heart,” exclaims 6-year-old John-Henry Lee to the many caregivers who’ve been by his side throughout his long hospital stay. John-Henry and his family had been waiting for a lifesaving heart transplant for six months before they received the news.
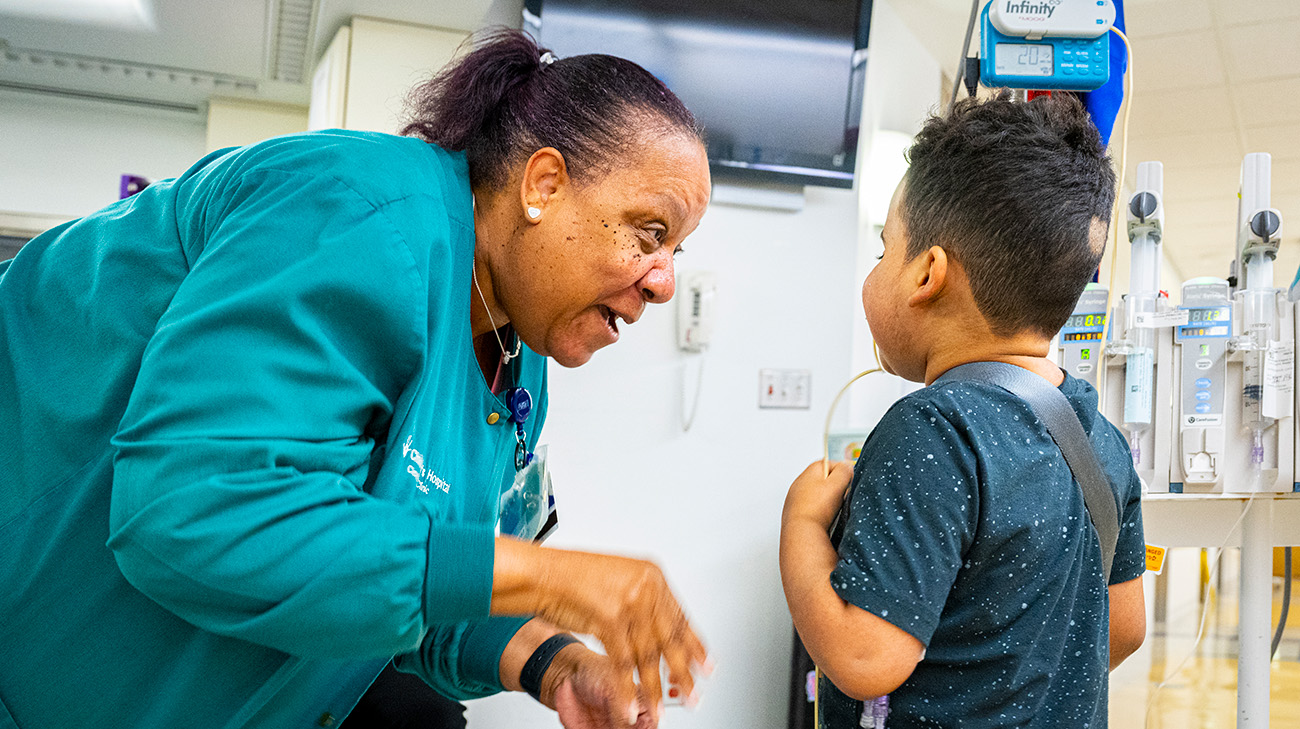
“When the transplant coordinator said they found his special heart, I immediately broke down,” says Sarah Lee, John-Henry’s mom. “I walked in the room teary-eyed to tell John-Henry, and when I told him, he said, ‘I have to go tell everybody.’”
Before John-Henry was born, Sarah learned he had hypoplastic left heart syndrome (HLHS), a rare congenital heart condition where one side of the heart doesn’t develop correctly. In a baby with HLHS, the heart’s left side is too small to pump enough blood to the rest of the body.
The day John-Henry found out he was getting a new heart, he told all his favorite caregivers, including patient care nurse assistant Phyllis Torbert. His mom, Sarah, says a patch of John-Henry’s hair fell out a few days before the news, leaving a heart-shaped outline. She thought it was a sign his heart was coming soon. (Courtesy: Cleveland Clinic)
“John-Henry was admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit as soon as he was born. He was 5 days old when he had his first open-heart surgery,” says Sarah.
Surgeons typically perform three separate operations to treat HLHS – the first being the Norwood procedure. This operation lets a baby’s right ventricle take over for an underdeveloped left ventricle and aorta. After surgery, the right ventricle pumps blood to the lungs to get oxygen. It also pushes blood with oxygen to the entire body.
“Once a baby is born with HLHS, something needs to be done relatively quickly – so John-Henry underwent the Norwood procedure in the first week of life,” explains his pediatric cardiologist Gerard Boyle, MD, pediatric heart function and transplant cardiologist at Cleveland Clinic Children’s. “Infants feel fine with that for some time, but then something changes. They need more oxygen as they start crawling and walking. That’s when we move on to the Glenn procedure.”
\
John-Henry underwent the Glenn procedure at 4 months old – his second open-heart surgery before even celebrating his first birthday. Dr. Boyle explains this provides blood flow for some additional time before the final surgery, the Fontan procedure, which is done when the child is between 18 months and 4 years old. The three operations put the heart’s workload on the right ventricle, but for John-Henry, it wasn’t enough.
“After the Fontan procedure, some patients can make it into adulthood before they need further palliation. However, other patients fail very early in their childhood, which was the case with John-Henry. His right ventricle was incapable of providing him with the circulation that was required, and so he was getting sicker and sicker,” says Dr. Boyle.
As John-Henry began experiencing heart failure, it became apparent a heart transplant was his only option. He was placed on the transplant waiting list in December 2023. From there, he spent Christmas, his sixth birthday, New Year’s and Easter in the hospital waiting for a new heart.
“Every holiday was just another holiday we celebrated in the hospital. We basically moved into his hospital room. At a certain point, you start thinking it’s not going to come,” says Sarah.

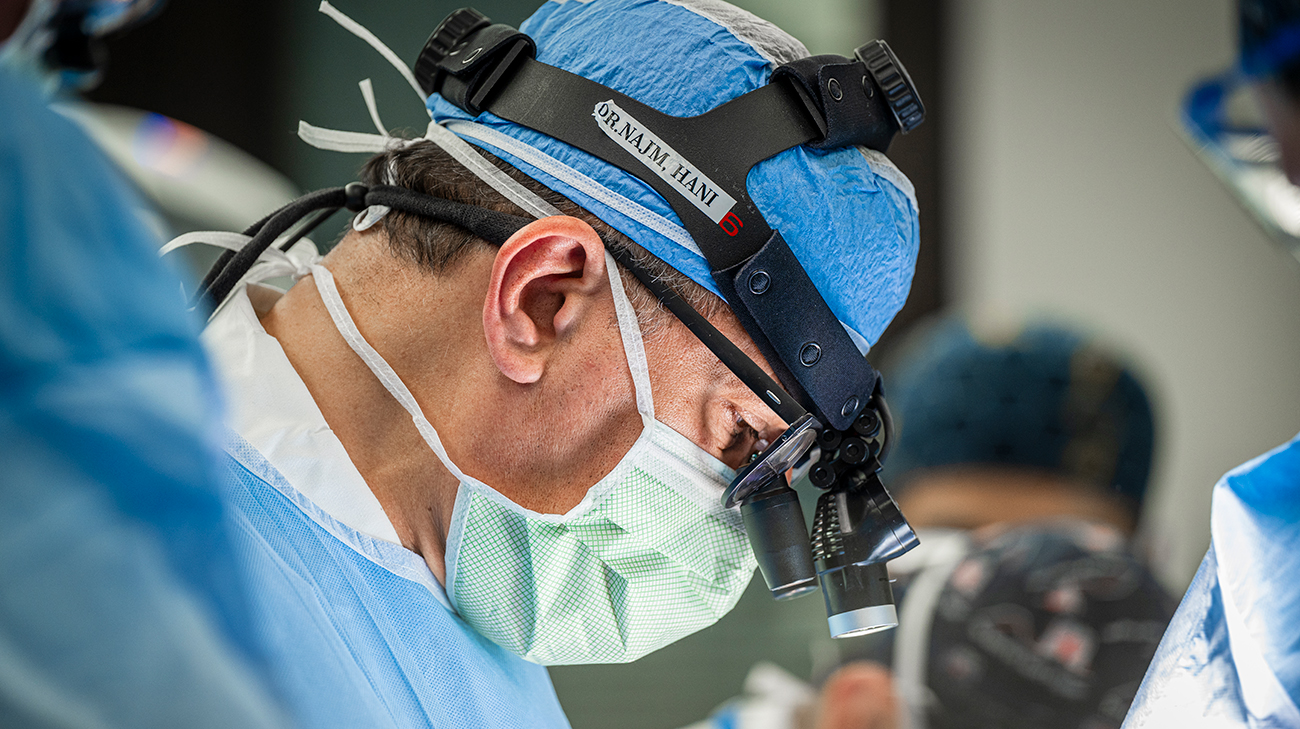
In May 2024, they got the news – a new heart had become available for John-Henry. The very next day, he underwent his heart transplant procedure performed by pediatric and congenital heart surgeon Hani Najm, MD, who had also performed all of John-Henry’s previous heart surgeries.
After his transplant, John-Henry started what would be a long recovery. He experienced gastroparesis (paralysis of the stomach), which affects your stomach nerves and muscles. It makes your stomach muscle contractions weaker and slower than they need to be to digest food and pass it on to your intestines. This made eating for John-Henry challenging. He also experienced transplant rejection.
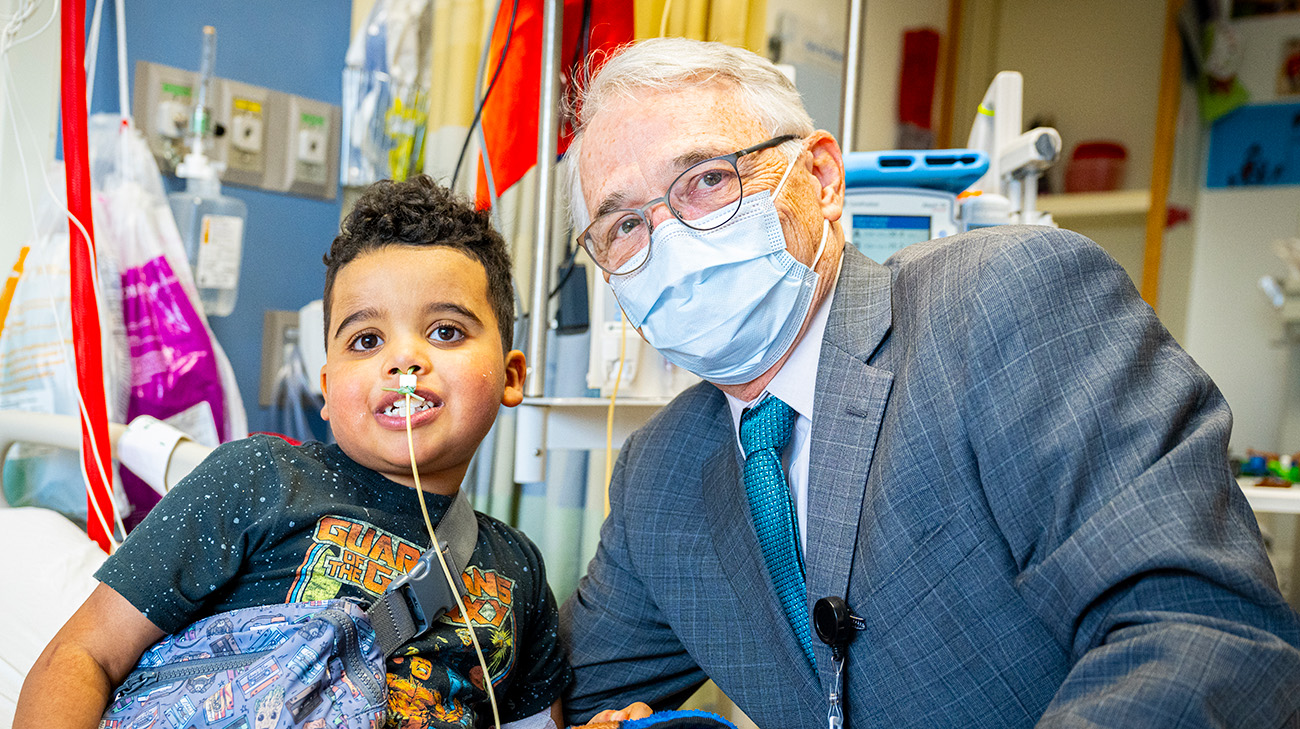

“John-Henry started tolerating his feeds being delivered through a nasogastric tube and will work his way back to feeding on his own again,” says Dr. Boyle. “When it comes to rejection, it’s unfortunate but not unexpected. We ramp up our surveillance looking for signs of rejection, and he experienced it in the amount of time we would anticipate. We were ready and able to start treating it aggressively.”
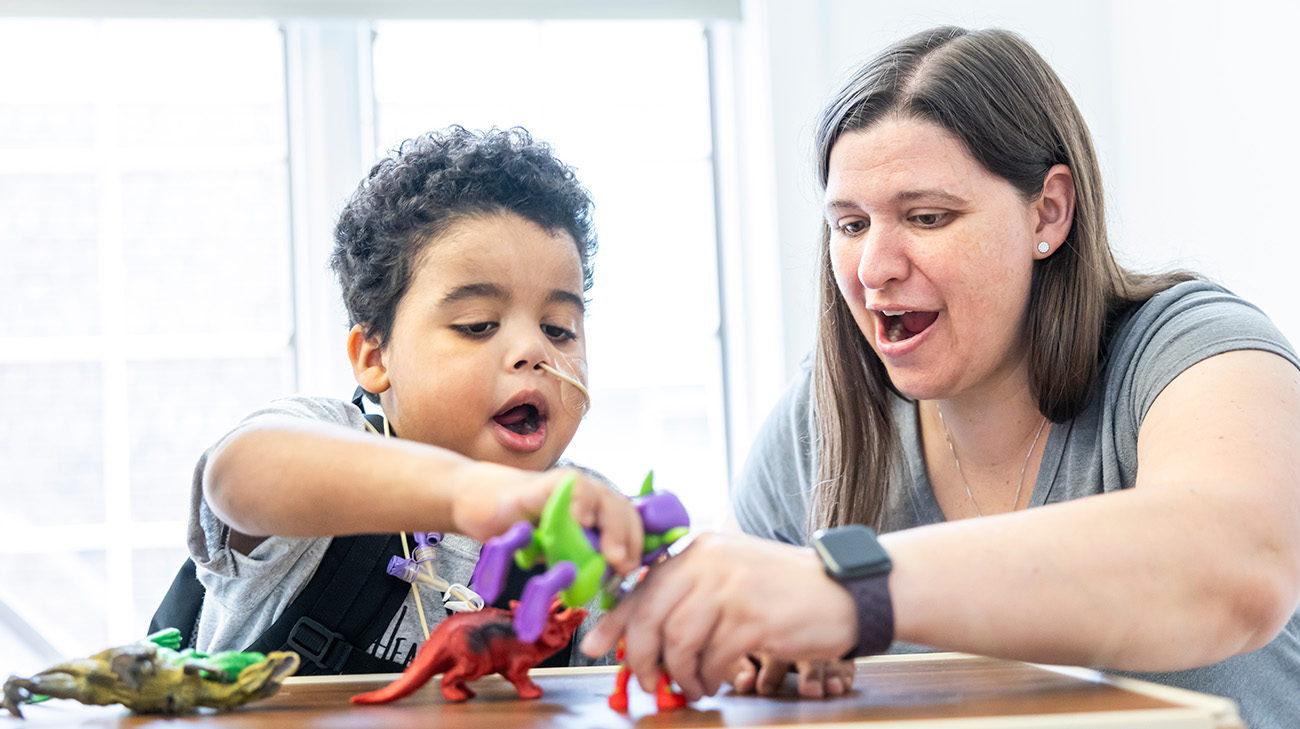
After more time spent in the hospital following his transplant, John-Henry was discharged to Cleveland Clinic Children’s Hospital for Rehabilitation to build back up his strength. Sarah says she’s starting to see her boy – who loves dinosaurs, battling with his animal and action figures, and making others smile – heal and become whole again.












